Hello, guys! Welcome to Grammar Zone! My name’s Harry Jones.
My best friends Allan and Kate will help me make our lessons useful and enjoyable.
Harry: I have been looking through some old photos just now and I’ve found one that dates back to 1980. It’s a photo of my parents. My parents have known each other since primary school and have been married for eighteen years. The two young people have changed a lot since then – Dad has lost most of his hair, for a start!
Back then, Dad had to carry his stack of heavy vinyl LP records from party to party! Nowadays I can fit hours of music in one tiny MP3 player. We also have mobile phones, Internet and digital cameras!
Yes, many things have changed, but on the other hand, have you ever thought about how some things have stayed the same?
Here is one photo of Mr Parker’s bakery. Everyone in my family loves his delicious cakes and he has been making them since 1962. Not far from the bakery, there’s a bookshop. It opened in 1911, so it has been selling books for more than a century!
I’ve found, have known, have changed, has lost, have thought, have stayed: Can you define the tense of these verbs?
Right, the Present Perfect Tense.
Have been looking, has been making, has been selling: Can you remember what tense forms they are?
The Present Perfect Continuous Tense.
In the lesson today we’ll revise the formation and use of the Present Perfect and the Present Perfect Continuous tenses.
First, complete the tables.
Now check the information.
Present Perfect
We form the Present Perfect Tense with the help of auxiliary verb have for I/you/we/they and has when we use he/she/it in the sentence and regular forms of the main verb (by putting the ending –ed to the main verb.) or irregular forms of the main verb (using the list of irregular verbs or learning them by heart).
I/We/You/They have changed.
He/She/It has lost.
We form negations by putting not between have/has and the main form of the verb.
I/We/You/They have not (haven’t) changed.
He/She/It has not (hasn’t) lost.
We form questions by putting have/has before the subject.
Have I/we/you/they changed?
Has he/she/it lost?
Now let’s revise the formation of the Present Perfect Continuous Tense.
We form the Present Perfect Continuous with the help of auxiliary verb have for I/you/we/they and has when we use he/she/it in the sentence, the 3rd form of the verb to be (been) and the main verb with the – ing suffix.
Pay attention to the spelling rules:
enjoy - enjoying
take – taking
cut – cutting
I/we/you/they have been looking.
He/she/it has been looking.
We form questions by putting have/has before the subject.
Have I/we/you/they been looking?
Has he/she/it been looking?
We form negations by putting not between have/has and been.
I/we/you/they have not (haven’t) been looking.
He/she/it has not (hasn’t) been looking.
Let’s compare the use of the Present Perfect and the Present Perfect Continuous.
The Present Perfect and the Present Perfect Continuous connect the past and the present.
1. The Present Perfect is used to describe an action which started in the past and continues up to the present. In this case we often use for and since.

My parents have known each other since primary school and have been married for eighteen years.
1. The Present Perfect Continuous shows the duration of an action which started in the past and continues up to the present.
Mr Parker has been making cakes since 1962. (He started his business many years ago and he is still doing it.)

2. The Present Perfect describes an action which has recently finished and whose result is visible in the present.
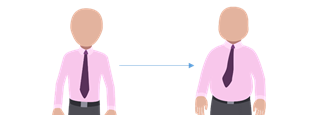
Mr. Simpson has put on some weight. (We see that he became bigger now.)
Dad has lost most of his hair. (He is almost bald.)
I’ve found an old photo of my parents. (I’m looking at it now.)
2. The Present Perfect Continuous is used for an action which started and finished
in the past and lasted! for some time. The result or effect of the action is visible in the present.
You’ve got paint on your clothes.
I’ve been working on my art project.
(He is no longer working, but the result of the action is visible – he’s got paint on his clothes.)
3. The Present Perfect shows an action which happened at an unstated time in the past. The exact time is not mentioned because it is either unknown or unimportant.
A new restaurant has opened near the cinema. (The exact time is not mentioned. What is important is the fact that there’s a new restaurant.).
Kevin has been to New York three times. (The exact time is unknown. What is important is the fact that he has visited New York three times.)
3. We use the Present Perfect Continuous to express anger, irritation or annoyance.
Have you been reading my emails again? (The speaker is angry.)

I’ve been waiting for you in the rain for two hours. Where have you been? (The speaker is irritated.)
4. The Present Perfect is also used for an action, which has happened within a time period, which is not over at the moment of speaking, such as today, this morning/afternoon/month/year, etc.
She has taken a lot of photos today. (The time period – today is not over yet. She may take more photos.)
But! She took a lot of photos yesterday. (The time period – yesterday - is over.)
4. We use the Present Perfect to talk about our experiences, something we have or haven’t done. We often use ever and never talking about experiences.
I’ve seen all his films.
Have you ever done an extreme sport?

She has never been on a hot air balloon flight.
5. With the verbs feel/like/ teach and work we can use either the Present Perfect or the Present Perfect Continuous with no difference in meaning.
He has lived/has been living here for twenty years.

6. Remember that state verbs do not have a continuous form!
She has known Martha for two years.
NOT She has been knowing Martha for two years.
Both the Present Perfect and the Present Perfect Continuous are used with the following time expressions:
how long
for (duration)
since (starting point)
lately/recently
The Present Perfect is usually used with the following time expressions:
already
yet (in negations and questions)
just
ever/never
so far
still (in negations)
Allan: Well, let’s sum up all the information of the lesson. Complete the tables with the terms proper either for Present Perfect or Present Perfect Continuous.
Let’s check.
Present Perfect: result, unknown/unimportant time, experience, unfinished period of time, state verbs.
Present Perfect Continuous: duration, annoyance/irritaion.
Harry: Okay, we’ve finished with the tenses.
If you’re interested in the history of your town, walk around and find out what hasn’t changed at all in the last thirty years, or even more. I’d like to know about more places like that. Send your emails to us.
 Получите свидетельство
Получите свидетельство Вход
Вход




 1230
1230

